A Deep Dive into Valve Cv: What It Means and Why It Matters for Flow Control
- marketing96225
- Jul 23, 2025
- 3 min read
What Is Valve Cv?
The Cv value, or flow coefficient, measures the capacity of a valve to pass fluid. Specifically, it represents the number of gallons per minute (GPM) of water at 60°F that will flow through a valve with a 1 psi pressure drop across it. The higher the Cv, the more flow the valve can handle.
In simpler terms, Cv tells you how much flow a valve can support, and it helps you compare valves based on their flow performance.
Example:
If a valve has a Cv of 5.0, it means 5 gallons of water per minute can pass through it with a 1 psi pressure drop.

Flow Coefficient Explained: Why Cv Matters
Understanding the flow coefficient is crucial because:
- It allows accurate valve sizing.
- It helps maintain system efficiency and performance.
- It reduces energy losses due to pressure drops.
- It ensures safety by preventing under- or over-sizing.
When choosing a brass valve, selecting one with the correct Cv ensures optimal flow without introducing inefficiencies or damaging sensitive components in the system.
Cv vs Kv: Whats the Difference?
If you're working in international or metric systems, you might encounter Kv instead of Cv.

To convert between Cv and Kv:
Kv = Cv x 0.865
Cv = Kv ÷ 0.865
Understanding Cv vs Kv is vital when reviewing international spec sheets or sourcing valves from global manufacturers.
Calculating Valve Flow Rate Using Cv
For liquids:

Where:
Q = Flow rate (GPM)
ΔP = Pressure drop (psi)
SG = Specific gravity of the fluid
For gases (simplified):
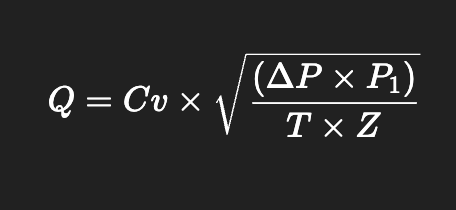
Where:
P₁ = Inlet pressure
T = Temperature (°R)
Z = Compressibility factor (typically close to 1)
Accurate calculating of valve flow rate helps system designers select the most efficient valve for the application.
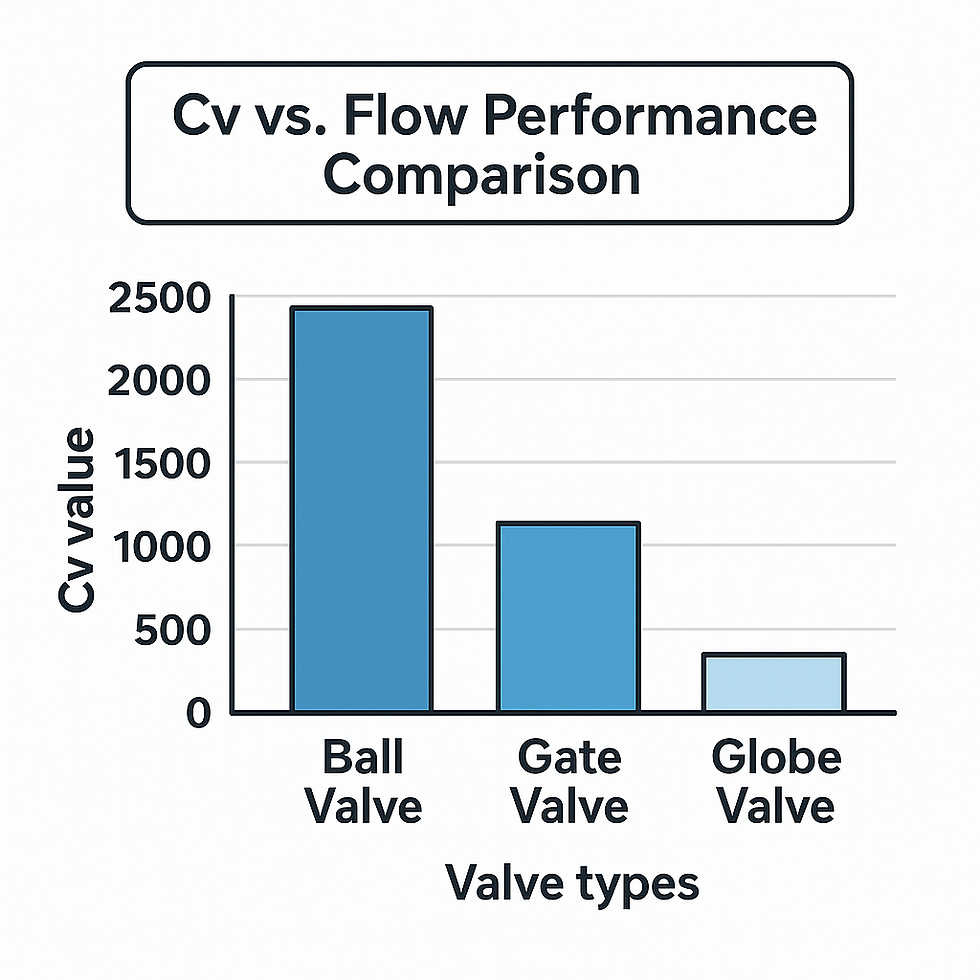
Cv Ratings in Brass Valves
Different valve types have different Cv values even at the same pipe size.
For example:

Brass ball valves typically offer the highest Cv values due to their full-port designs
Choosing the Right Cv for Your Application
Selecting a valve with the proper Cv depends on:
- Pipe diameter
- Fluid type and temperature
- Desired flow rate
- Acceptable pressure drop
At Enolgas USA, our technical team helps contractors, engineers, and OEMs select the right brass valves with Cv ratings optimized for their system requirements.
Final Thoughts
The brass valve Cv rating is more than just a number, it's a key factor that directly impacts your system's flow efficiency, energy consumption, and overall performance.
For help selecting valves with the optimal Cv rating for your application, contact Enolgas USA, your trusted partner in precision flow control.




Comments